By: Rachel D. Ramos G11-Neon
Online games became popular, while studies of Internet gaming addiction emerged, outlining the negative consequences of excessive gaming, its prevalence, and associated risk factors.It is argued that only by understanding the appeal of Internet gaming, its context, and neurobiologic correlates can the phenomenon of Internet gaming addiction be understood comprehensively. The aim of this review is to provide an insight into current perspectives on Internet gaming addiction using a holistic approach, taking into consideration the mass appeal of online games, the context of Internet gaming addiction, and associated neuroimaging finding.
The cited research indicates that the individual’s context is a significant factor that marks the dividing line between excessive gaming and gaming addiction, and the game context can gain particular importance for players, depending on their life situation and gaming preferences. Moreover, the cultural context is significant because it embeds the gamer in a community with shared beliefs and practices, endowing their gaming with particular meaning. The cited neuroimaging studies indicate that Internet gaming addiction shares similarities with other addictions, including substance dependence, at the molecular, neurocircuitry, and behavioral levels. The findings provide support for the current perspective of understanding Internet gaming addiction from a disease framework. The benefits of an Internet gaming addiction diagnosis include reliability across research, destigmatization of individuals, development of efficacious treatments, and the creation of an incentive for public health care and insurance providers. The holistic approach adopted here not only highlights empirical research that evidences neurobiologic correlates of Internet gaming addiction and the establishment of a preliminary diagnosis, but also emphasizes the necessity of an indepth understanding of the meaning, context, and practices associated with gaming.

Internet gaming is a booming market. In 2012, more than one billion individuals played computer games, which fuelled the 8% growth of the computer gaming industry in the same year.Massively Multiplayer Online games (MMOs) offer the possibility to play together with many other players and can be differentiated based on game content and player experience. A latent profile analysis of survey data from 4,374 Hungarian online gamers (91% male, mean age 21±6 years) indicated that the most prominent MMOs were role-playing games, first-person shooters, real-time strategy, and other games.
First, achievement includes advancing in the game, namely progressing via leveling up, acquiring status and power in the game, the game’s mechanics, including the possibilities for optimizing game play, and competition, including challenging and dominating others. Reputation and admiration from the gaming community for gaming achievements are further key factors motivating players to keep playing. The game mechanics or structural characteristics have been claimed to reinforce the potentially addictive qualities of games because they contribute to initiation, development, and maintenance of gaming.Second, the social factor is composed of socializing, including chatting and making new friends in the game, forming new relationships, and working in a team.Research suggests that the social element in MMORPGs is particularly important for gamers because it is an integral component of the enjoyment of playing. Moreover, it denotes a complex interaction between real and virtual social networks, further blurring the boundaries between these networks, making MMORPGs inherently social spaces.
Third, immersion in the game is denoted by discovery, ie, exploring the game and “hidden” game content, role-playing via one’s avatar, customization of one’s online character (such as sex, race, profession, appearance), and escapism, ie, playing in order to avoid real life. Escapism is an aspect of mood modification whereby individuals suffering from addictions induce a subjective shift in their mood by way of engaging in an addictive behavior, making the latter a coping strategy to deal with everyday problems.
The variety of gaming motivations satisfied by MMOR-PGs indicates that these types of games are particularly versatile because they can be tailored to individual players with different game preferences. Consequently, one could assume that there are many ways that might lead some individuals to get hooked on MMORPGs. In a sample of 696 MMORPG players (93% male, mean age 26±7.4 years), achievement, socializing, and escapism motivations were found to be predictive of addictive play, together with sex accounting for 19% of variance in the MMORPG addiction score.14 Similarly, in a sample of 175 primarily Dutch MMORPG players (87% male, mean age 21±6.5 years), escapism and game mechanics predicted excessive gaming over and above the contribution of the time spent gaming, together explaining 46% of the variance in problematic gaming. In a nutshell, the mass appeal of MMORPGs rests on their versatility because they are tailored to gamers young and old, male and female, who have different game preferences. MMORPGs are particularly good at meeting various players’ different needs. This mass appeal may have contributed to findings from research which indicate that online games, and specifically MMORPGs, are more addictive than any other types of both offline and online games15 because they reward players on partial reinforcement schedules, leading to maintenance of play
Internet gaming addiction
In recent years, research about Internet gaming addiction has increased both in quantity as well as in quality. Research on gaming addiction dates back to 1983, when the first report emerged suggesting that video gaming addiction is a problem for students. Shortly thereafter, the first empirical study on gaming addiction was published by Shotton, based on self-reports of young male players who claimed they were “hooked” on their games. The early studies suffered from a lack of standardized psychometric instruments used for assessing gaming addiction. However, research indicates that self-reports correlate with standardized measures. Following on from that, further studies were carried out in the 1990s, initially assessing gaming addiction based on the criteria for pathologic gambling as stipulated in the third and fourth editions of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders (DSM).Although similar, pathological gambling and excessive gaming do not present with the same clinical picture, and some have argued that using the diagnostic criteria for pathological gambling in order to diagnose pathological gaming only taps into obsessive use and preoccupation rather than actual psychopathology.In the 2000s, online games became popular, while studies of Internet gaming addiction emerged
The studies on Internet gaming addiction in the new millennium reported prevalence estimates which vary significantly and range from 0.2% in Germany to 50% of Korean teenagers. This discrepancy in estimates is due to various conceptualizations, diverse measurement instruments, as well as the different cutoff points used. Further, dissimilar constructs (“Internet gaming addiction”, “dependence”, “problematic”, and “excessive play”) are measured in various samples (children, adolescents, gamers) and cultures. In most studies, self-reports have been used, which puts the reliability and validity of the potential diagnosis in question. However, research indicates that self-diagnosis correlates with standardized measures of addiction, suggesting that the individual’s perception of problems can be relatively accurate.
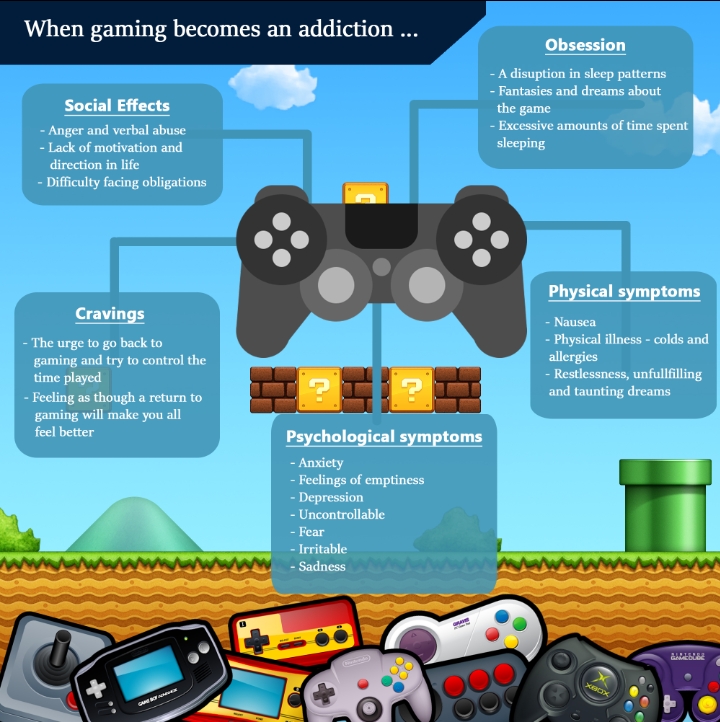
The concerns appear to be grounded as a growing number of studies indicate that Internet gaming addiction is associated with various negative consequences. The psychological consequences include the following: sacrificing real-life relationships, other pastime activities, sleep, work, education, socializing, and relationships,obsession with gaming and a lack of real-life relationships,lack of attention,aggression and hostility stress dysfunctional coping worse academic achievement problems with verbal memory and low well-being and high loneliness.Moreover, psychosomatic consequences have been found in a number of studies. These included problems with sleeping seizures and psychosomatic challenges. This long list indicates that Internet gaming problems must be taken seriously as they can affect the individual negatively in a variety of ways.
Internet gaming addiction is a behavioral problem that has been classified and explained in numerous ways. According to Griffiths,13 biopsychosocial processes lead to the development of addictions, such as Internet gaming addiction, which include the following components. First, the behavior is salient (the individual is preoccupied with gaming). Second, the individual uses the behavior in order to modify their mood (ie, gaming is used to escape reality or create the feeling of euphoria). Third, tolerance develops (the individual needs increasingly more time to feel the same effect). Fourth, withdrawal symptoms occur upon discontinuation of the behavior (the individual feels anxious, depressed, and irritable if they are prevented from playing). Fifth, interpersonal and intra-personal conflict develops as a consequence of the behavior (the individual has problems with their relationship, job, and hobbies, and lack of success in abstinence). Finally, upon discontinuation of the behavior, the individual experiences relapse (they reinitiate gaming).
Complete Your Work First
Research has shown that student gamers spend 30% less time reading and 34% less time on their homework. Therefore, it is important that student gamers set up healthy routines, where they only allow themselves to play games once they have completed the necessary work.
Don’t: Lose Sleep Over it
Many adolescents are choosing to continue playing video games late into the night, with studies showing that 24% of adolescents are gaming after 9pm. Gaming late into the night has been associated with higher levels of daytime sleepiness and an increase in the time taken to fall asleep, particularly if games are violent.
Set a Time Limit
Students need to manage their time to ensure that they are not spending all their time gaming. One way in which students can manage their time effectively is by setting up a timetable, where they schedule in what they would like to achieve in the upcoming week.
Don’t: Spend Too Much Time Alone in Your Room Gaming
Students need to ensure that gaming is not isolating them and having a negative impact on their social skills or the quality of their relationships with their peers and parents. Students need to remember that social interactions and having friends and family around them is important as they can offer essential support, guidance and companionship in times of need.
We need to care out health don’t get addict to games or to our gadget use it for important thing only.If you are parent and have a 1-10 years old child don’t let them hold a gadget to avoid addiction show them a good moral and teach them right before using a gadget.Addiction on games does not good for our body and mental health its effect the other things that we need to do first so control using gadget to avoid online games addiction.